In the realm of data management and disaster recovery, the concept of local continuous replication (LCR) stands as a beacon of reliability and resilience. As businesses navigate the complexities of modern technology landscapes, ensuring the uninterrupted flow of critical data has become non-negotiable. LCR emerges as a solution designed to address this imperative with precision and efficiency.
At its core, LCR embodies the proactive approach to data protection, offering real-time replication of data within a localized environment. Unlike traditional backup methods that rely on periodic snapshots, LCR operates seamlessly, continuously mirroring data from a primary source to a secondary destination. This dynamic replication not only minimizes the risk of data loss but also reduces recovery time objectives (RTOs) to mere moments, if not seconds.
Understanding the Concept of Data Replication
What is Data Replication?
Data replication refers to the process of creating and maintaining copies of data across multiple storage devices or locations. The primary goal of data replication is to enhance data availability, improve disaster recovery capabilities, and facilitate data distribution for various purposes such as analytics and reporting.
Importance of Data Replication in Business Continuity
In today’s interconnected world, businesses cannot afford prolonged downtime or data loss. Data replication plays a crucial role in ensuring business continuity by providing redundancy and resilience against unexpected disruptions.
Explaining Local Continuous Replication (LCR)
Definition of LCR
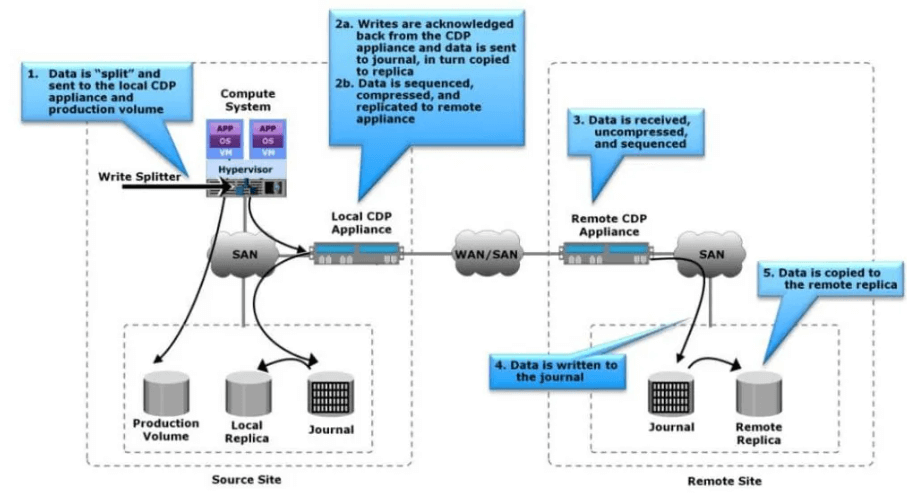
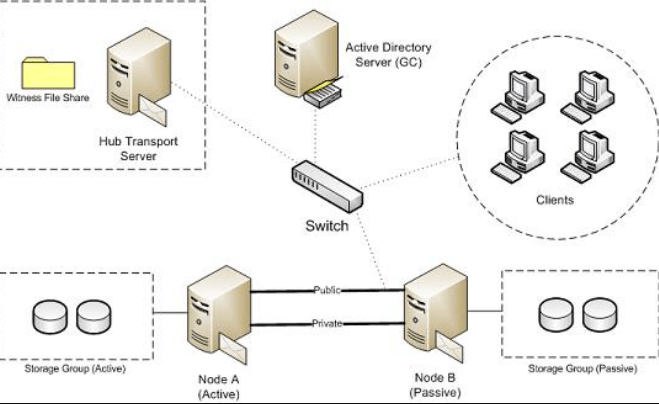
LCR is a form of synchronous data replication wherein data changes are mirrored in real-time or near real-time from a primary storage system to a secondary storage system located in close proximity. This approach offers rapid recovery capabilities and minimal data loss in the event of a primary system failure.
How LCR Works
LCR operates by continuously monitoring changes to the data on the primary storage system and replicating those changes to the secondary storage system. This process typically involves the use of specialized software or hardware solutions that facilitate data synchronization across the two locations.
Advantages of Implementing LCR
Data Protection
LCR provides robust data protection by ensuring that critical business data is replicated in real-time, minimizing the risk of data loss due to hardware failures, software errors, or cyber threats.
Reduced Downtime
By maintaining a synchronized copy of data in a secondary location, LCR enables rapid failover in the event of a primary system failure, thereby reducing downtime and minimizing the impact on business operations.
Cost-effectiveness
Compared to traditional disaster recovery solutions that involve off-site backups or colocation facilities, LCR offers a cost-effective approach to data replication, especially for organizations with limited IT budgets.
Challenges and Limitations of LCR
Dependency on Local Infrastructure
LCR is inherently tied to the availability and reliability of local infrastructure, making it susceptible to regional disasters or network outages that may affect both primary and secondary storage systems.
Limited Scalability
While LCR is well-suited for small to medium-sized environments, it may pose scalability challenges for large-scale deployments or distributed architectures due to bandwidth constraints and performance overhead.
Best Practices for Implementing LCR
Assessing Data Criticality
Prioritize data based on its criticality to business operations and allocate resources accordingly to ensure that essential data is replicated with minimal latency.
Regular Testing and Monitoring
Conduct regular tests and simulations to validate the effectiveness of LCR implementation and identify any potential issues or bottlenecks proactively. Implement robust monitoring tools to track replication status and performance metrics.
Disaster Recovery Planning
Integrate LCR into comprehensive disaster recovery plans that encompass risk assessment, mitigation strategies, and recovery procedures to minimize downtime and data loss in crisis situations.
Comparing LCR with Other Data Replication Methods
LCR vs. Remote Data Replication
Unlike remote data replication, which involves copying data to a geographically distant location, LCR focuses on replicating data within the same geographical area, offering lower latency and higher performance for local operations.
LCR vs. Asynchronous Replication
While asynchronous replication allows for more flexibility in data transfer and can tolerate longer latency, LCR provides synchronous replication with minimal data loss, making it ideal for applications requiring strict RPO (Recovery Point Objective) requirements.
Real-world Applications of LCR
Small and Medium-sized Businesses (SMBs)
LCR offers an affordable and efficient data protection solution for SMBs that may lack the resources or infrastructure to implement complex disaster recovery strategies.
Enterprise-level Organizations
Large enterprises can leverage LCR to complement their existing data replication and disaster recovery initiatives, enhancing data availability and minimizing the risk of downtime across distributed environments.
Future Trends in Local Continuous Replication
Integration with Cloud Services
As organizations embrace cloud computing for its scalability and flexibility, we can expect to see greater integration between LCR solutions and cloud-based storage platforms, enabling seamless data replication and disaster recovery in hybrid IT environments.
Automation and AI-driven Solutions
Advancements in automation and artificial intelligence will empower LCR solutions to automate tasks such as data prioritization, failover orchestration, and performance optimization, thereby streamlining operations and enhancing resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions On Local Continuous Replication
1.What is local continuous replication (LCR) and how does it differ from other data replication methods?
LCR is a form of data replication that involves continuously mirroring data changes from a primary storage system to a secondary storage system within the same geographical area. How does this differ from other methods like asynchronous replication or remote data replication.
2.How does LCR contribute to ensuring data continuity and business resilience?
LCR ensures near real-time replication of data, minimizing the risk of data loss in the event of hardware failures or disasters. How does this real-time replication enhance data continuity and contribute to business resilience compared to traditional backup methods.
3.What are the primary benefits of implementing LCR in a business environment?
Implementing LCR offers several benefits, including reduced downtime, improved data protection, and cost-effectiveness. How do these benefits impact business operations and overall efficiency.
4.What challenges or limitations might organizations face when deploying LCR solutions?
Despite its advantages, organizations may encounter challenges such as dependency on local infrastructure and scalability issues. What strategies can organizations employ to overcome these challenges and maximize the effectiveness of LCR.
5.How does LCR support disaster recovery efforts in case of system failures or data loss?
LCR plays a crucial role in disaster recovery by providing rapid failover capabilities and minimizing data loss. What mechanisms does LCR employ to ensure quick recovery and seamless continuity of operations during critical incidents?
conclusion
local continuous replication (LCR) stands as a formidable solution in the realm of data management, offering businesses unparalleled levels of data protection, resilience, and continuity. Through its real-time replication capabilities and cost-effective implementation, LCR addresses critical challenges faced by organizations in safeguarding their data assets against unforeseen disasters and system failures. Despite potential challenges, such as scalability and infrastructure dependency, the benefits of LCR in minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity far outweigh its limitations. As businesses continue to navigate the complexities of a digital landscape, embracing LCR as a cornerstone of their data replication strategies will undoubtedly bolster their resilience and readiness to withstand the ever-evolving threats to data integrity.








